Oh my SSH 😲
July 26, 2019
3 minutesSSH, also known as secure shell or secure socket shell is a protocol that establishes secure connection between a client and a server. It makes use of various cryptographhy techniques to establish a secure, encrypted connection between two parties(client and server).
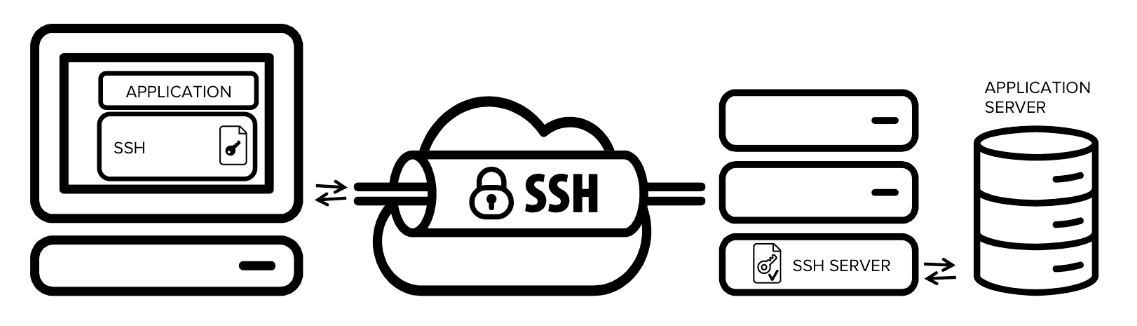
How SSH works?
SSH protocol uses symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption and hashing in order to secure transmission of information. An SSH session is established in two separate stages. During the first stage, the server and the client agree upon a session key to encrypt and protect future communication. The next stage is to authenticate the user and discover whether to allow him access the server.
1. Agreeing upon a session key:
The client initiates a SSH connection with the server. Server listens to default port 22(this port can be changed) for SSH connections.The server also provides its public host key, which the client can use to check whether this was the intended host.
After the server is verified, both parties agree on a session key using a version of Diffie–Hellman key exchange algorithm. Both parties contribute equally in key-generation as outlined by the algorithm.
The generated secret is a symmetric key, meaning that the same key is used to both encrypt and decrypt the message. This session key is used to wrap all further communication in an encrypted tunnel that cannot be decrypted by others.
2. Authenticating user’s access to the server:
The next stage involves authenticating the user and deciding access.Authentication is done using SSH key pair(public and private key). Public key is used for data encryption and can be shared.Private key however is to be kept secret and is used to decrypt data. The authentication process happens in following steps:
- The client begins by sending an ID(public key) for the key pair it would like to authenticate with to the server.
- The server check’s the
authorized_keysfile of the account that the client is attempting to log into for the key ID.If a public key with matching ID is found in the file, the server generates a random number and uses the public key to encrypt the number. - The server sends the client this encrypted message.If the client actually has the associated private key, it will be able to decrypt the message using that key, revealing the original number.
- The client combines the decrypted number with the shared session key that is being used to encrypt the communication, and calculates the MD5 hash of this value and sends this MD5 hash back to the server.
- The server uses the same shared session key and the original number that it sent to the client to calculate the MD5 value on its own. Both MD5 hashes are compared and if those values match, it proves that the client was in possession of the private key and the client is authenticated.
References: